Fortinet FortiWeb Authentication Bypass via Path Traversal Vulnerability (CVE-2025-64446)
Rapid Response Advisory
A critical authentication bypass vulnerability in Fortinet FortiWeb allows an unauthenticated attacker to add new administrative users on vulnerable appliances. This vulnerability was unknown but actively exploited as early as October, and Fortinet released a security advisory for it on November 14, 2025. The vulnerability was also added to the CISA KEV catalog the same day. Given active exploitation observed, organizations should run the Rapid Response test to find exploitable instances and apply the mitigations below immediately.
What It Is and Why It Matters
FortiWeb is Fortinet’s web application firewall (WAF) and reverse-proxy appliance used to protect web applications, terminate TLS, and apply web/HTTP security policies at the network edge for enterprises and service providers. The product is designed to protect against attacks and offers additional detection capabilities via a web-specific vulnerability scanner.
Stop Guessing, Start Proving
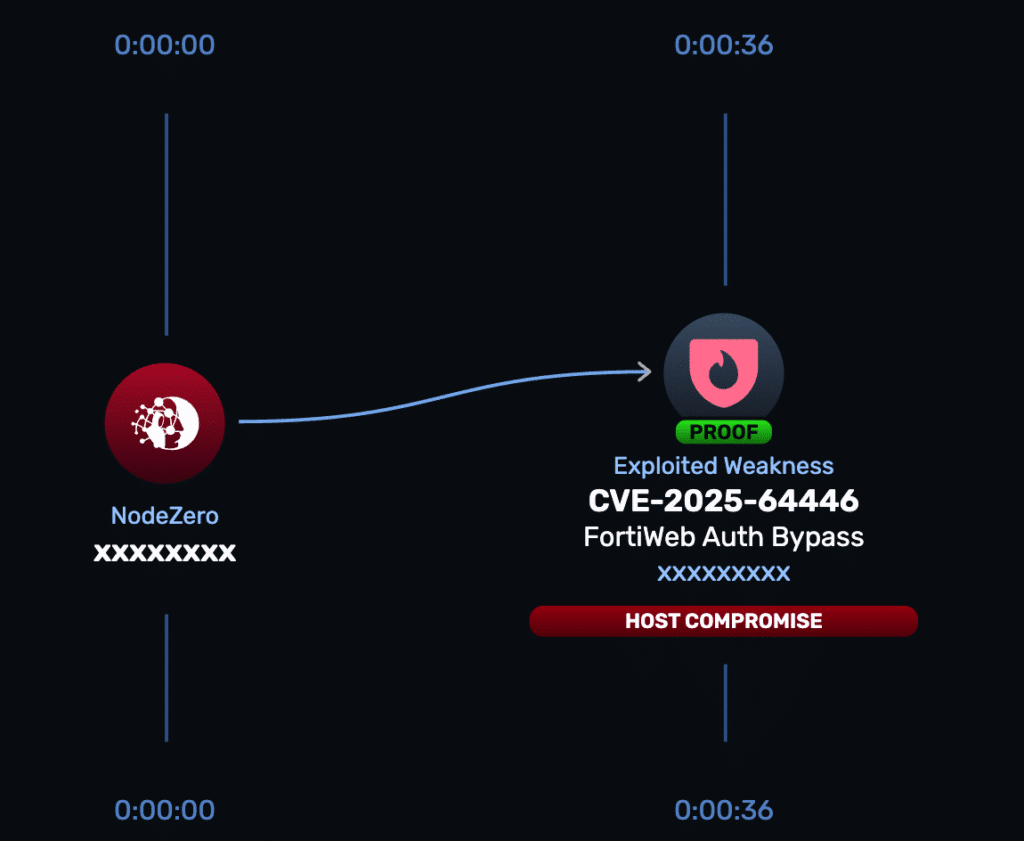
CVE-2025-64446 is a path-traversal / authentication-bypass flaw in FortiWeb that can be abused by unauthenticated attackers to create new administrative users on vulnerable appliances, granting full appliance control (admin UI, config, policies, logs). This lets attackers weaken protections, harvest credentials/configs, and pivot into behind-the-WAF networks.
The issue affects this endpoint: /api/v2.0/cmdb/system/admin%3f/../../../../../cgi-bin/fwbcgi and HTTP POST payloads to this path can generate the new admin accounts.
- Unauthenticated admin user creation: Attackers can abuse an authentication bypass to arbitrarily create administrative accounts, enabling full control of the FortiWeb appliance.
- High operational risk: With admin access, an attacker can alter security policies, exfiltrate sensitive configurations, pivot further into internal networks, and establish persistence.
- Active exploitation has been observed as early as October. Because exploit attempts are sprayed broadly against internet-exposed FortiWeb devices, unpatched and internet-reachable appliances are at immediate, high risk and should be treated as urgent and patched as quickly as possible.
NodeZero Offensive Security Platform: Rapid Response Test
The Fortinet FortiWeb Rapid Response test enables customers to safely find exploitable instances and focus remediation efforts on proven at-risk assets.
- Validate with NodeZero Rapid Response test:
Run the test to confirm whether your FortiWeb instances are currently exploitable. - Mitigate immediately:
Prioritize patching exploitable instances. Apply mitigations if you can’t immediately patch. - Re-run Rapid Response test:
Confirm you’re no longer exploitable to verify your mitigation or remediations worked.
Additional Recommended Actions
- Restrict management access: Limit FortiWeb Web Portal exposure to specific IP ranges or VPN; remove public internet exposure where possible.
- Harden and monitor the admin API and account creation: Instrument detections for traffic to
/api/v2.0/cmdb/system/adminand block suspicious traffic patterns at upstream controls if feasible. Monitor user creation events. - Tighten identity controls: Enforce MFA for all administrative access paths where supported; rotate administrative credentials and API tokens if compromise is suspected.
- Increase audit frequency: Temporarily increase the cadence of admin/audit log reviews and alerting thresholds to catch rapid changes.
Affected Versions and Patching
Product: Fortinet FortiWeb
Affected and Patched Versions
| Version | Affected | Patched |
| FortiWeb 8.0 | 8.0.0 – 8.0.1 | 8.0.2 |
| FortiWeb 7.6 | 7.6.0 – 7.6.4 | 7.6.5 and above |
| FortiWeb 7.4 | 7.4.0 – 7.4.9 | 7.4.10 and above |
| FortiWeb7.2 | 7.2.0 – 7.2.11 | 7.2.12 and above |
| FortiWeb 7.0 | 7.0.0 – 7.0.11 | 7.0.12 and above |
If you cannot immediately patch, disable HTTP or HTTPS for internet facing interfaces. Fortinet recommends taking this action until an upgrade can be performed. If the HTTP/HTTPS Management interface is internally accessible only as per best practice, the risk is significantly reduced.
Detection and monitoring guidance
- Log sources to review
- FortiWeb administrative access logs and audit logs.
- Reverse proxy/WAF logs in front of FortiWeb (if applicable).
- Network telemetry for management interfaces.
- High‑signal indicators
- HTTP requests to
/api/v2.0/cmdb/system/adminwith methods such as POST/PUT from unknown or untrusted IPs. - Creation of new administrative users or privilege elevation on existing accounts.
- Failed/odd authentication events followed by successful admin actions.
- Unusual admin activity outside normal maintenance windows.
- HTTP requests to
- Initial triage steps
- Enumerate all current admin users and compare against an authorized baseline.
- Review recent configuration changes, policy edits, and audit trails tied to admin accounts.
- Isolate management interfaces behind VPN/allow‑lists if not already restricted.
Risk scenarios to consider
- Persistence via shadow admins: Attackers add hidden or innocuous‑looking admin accounts that survive basic clean‑ups.
- Policy manipulation: Malicious changes weaken upstream protections, enable data exfiltration paths, or create blind spots.
- Lateral movement: Compromised FortiWeb may be used to discover internal assets and pivot deeper into the environment.
Timeline
- October 6, 2025: Initial exploitation observed on the then unassigned CVE
- November 12, 2025: Renewed attention on the vulnerability
- November 14, 2025: Fortinet releases advisory confirming vulnerability and patches
- November 14, 2025: Newly-assigned CVE-2025-64446 is added to CISA KEV