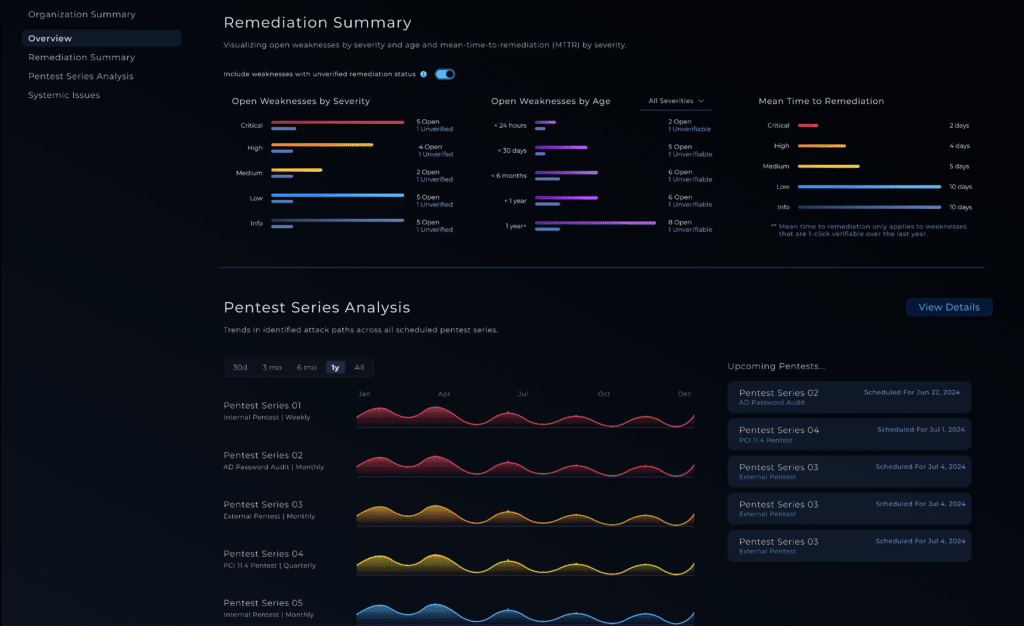
Oracle Identity Manager Pre-Auth RCE | CISA KEV
CVE-2025-61757 is a critical pre-authentication remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in the REST WebServices component of Oracle Identity Manager (OIM), part of Oracle Fusion Middleware. Supported versions 12.2.1.4.0 and 14.1.2.1.0 are affected.
Assigned a CVSS 3.1 score of 9.8, the flaw allows an unauthenticated attacker on the network to bypass REST authentication filters using crafted URL suffixes and reach privileged endpoints that enable arbitrary code execution.
Oracle released a fix in the October 21, 2025 Critical Patch Update (CPU).
CISA added the vulnerability to the KEV list after validating active exploitation. Earlier scan activity observed between August 30 and September 9, 2025—initially thought to be exploitation—was later attributed to research activity, but exploitation is now confirmed.
Stop Guessing, Start Proving
Technical Details
- Root Cause
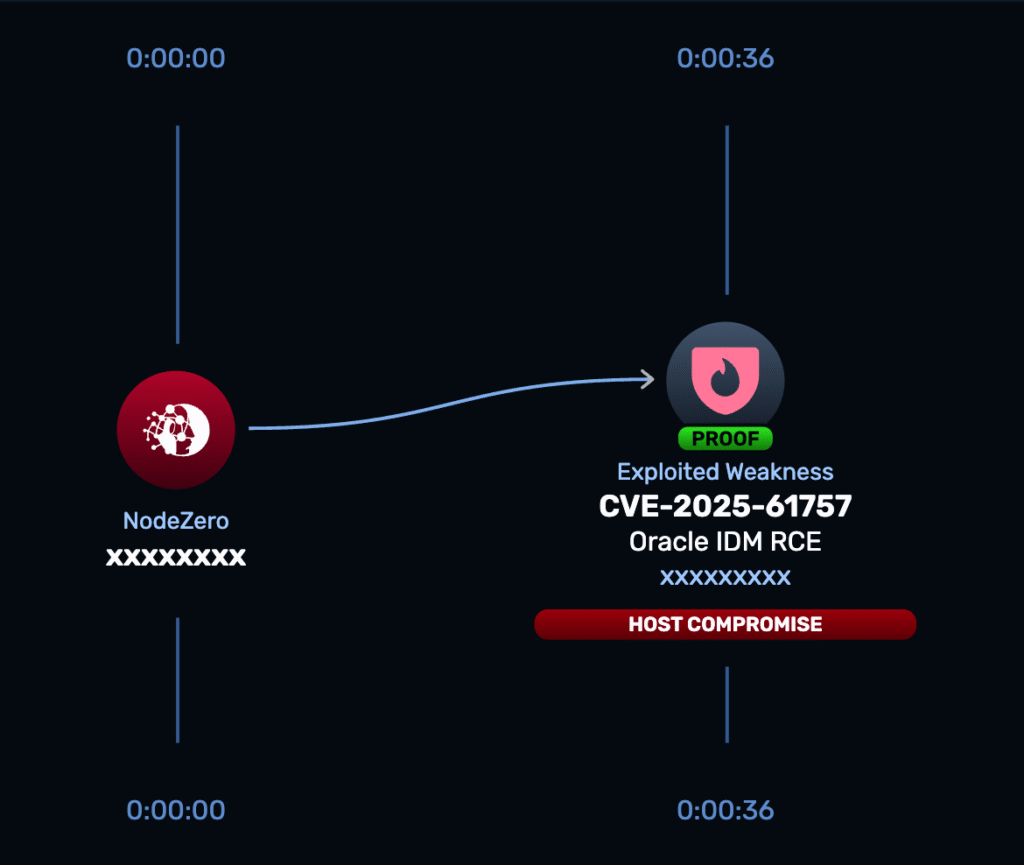
By appending metadata-style suffixes such as;.wadlor?WSDLto REST URIs, an attacker can bypass the authentication filter and reach protected API handlers. - RCE Path
After bypassing the filter, an attacker can reach an exposed Groovy script endpoint that is meant for checking Groovy code. By writing an annotation that executes at compile time, researchers were able to execute arbitrary code. - Impact
Full compromise of the OIM server, including the ability to:
- Modify or create privileged accounts
- Tamper with provisioning workflows
- Interfere with MFA, SSO, or downstream identity systems
- Establish persistence on the WebLogic/OIM host
- Move laterally into connected directories and SaaS identity integrations
Because OIM centrally manages identity lifecycle and entitlements, exploitation can result in widespread access escalation across the enterprise.
NodeZero® Offensive Security Platform — Rapid Response
1. Run a Rapid Response Test
Use the Oracle Identity Manager CVE-2025-61757 Rapid Response test to determine whether affected OIM instances—internal or internet-facing—are exploitable in your environment.
2. Patch Immediately
Apply Oracle’s October 2025 Critical Patch Update for Identity Manager versions 12.2.1.4.0 and 14.1.2.1.0.
Follow Oracle’s SPB tooling and CPU guidance to ensure all prerequisites are met.
3. Re-run the Rapid Response Test After Patching
Verify that OIM instances are no longer exploitable.
Indicators of Compromise
| Indicator | Type | Description |
Requests to OIM REST endpoints with ;.wadl or ?WSDL | Network | Look for anomalous HTTP access to /iam/governance/* or similar REST paths ending in metadata suffixes. |
Unusual traffic to /iam or REST admin endpoints | Network | Especially from foreign IPs, TOR/VPN sources, or after-hours administrative activity windows. |
| Groovy compilation endpoint access | Network / App Logs | Requests initiating compilation actions or containing suspicious Groovy syntax. |
| JVM child processes | Host | java or WebLogic spawning shell processes or script interpreters. |
| Unexpected privileged account creation | Identity | Sudden changes in entitlements, role assignments, or workflow states originating from OIM. |
| New outbound connections from OIM hosts | Network | Connections to unfamiliar external endpoints following suspicious REST requests. |
Affected Versions & Patch
Affected Versions
- Oracle Identity Manager 12.2.1.4.0
- Oracle Identity Manager 14.1.2.1.0
Patch
- Fixed in Oracle Critical Patch Update (CPU) — October 21, 2025
- Apply the CPU or stack patch bundle (SPB) for your environment
- Ensure WebLogic and database prerequisites are satisfied
Timeline
- August 30 – September 9, 2025: Scan activity consistent with the exploit observed (later attributed to researcher activity).
- October 21, 2025: Oracle releases CPU including fix for CVE-2025-61757.
- November 21, 2025: CISA adds CVE-2025-61757 to the KEV catalog.
- November 24, 2025: NodeZero Rapid Response test becomes available.
References
🔗 Oracle Critical Patch Update Advisory — October 2025
🔗 NVD Entry for CVE-2025-61757
🔗 CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog
🔗 Searchlight Cyber Technical Analysis
🔗 Public Reporting: The Hacker News