React Server Components Remote Code Execution | Rapid Response**
CVE-2025-55182, widely referred to as React2Shell, is a maximum-severity unauthenticated remote code execution vulnerability in the React Server Components Flight protocol. The flaw affects React 19, Next.js App Router and any framework or bundler that integrates React Server Components.
Multiple China-nexus threat groups have already begun exploiting the vulnerability, and CISA has added it to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. Many proof-of-concept exploits have hit the web, many of which aren’t valid and shouldn’t be used.
A safe-for-production Rapid Response test that does prove exploitability is available, so security teams can determine whether their deployments are actually at risk and verify the effectiveness of mitigation and patching efforts.
What it is and why it matters
React Server Components use the Flight protocol to serialize and transmit component structures between server and client. Frameworks such as Next.js, Remix, React Router RSC, Waku, Vite RSC plugin, Parcel RSC plugin and RedwoodSDK integrate these server packages.
React powers millions of websites, and Next.js is widely deployed across modern web applications. Tens of thousands of exposed endpoints remain vulnerable, and several organizations have already confirmed compromises.
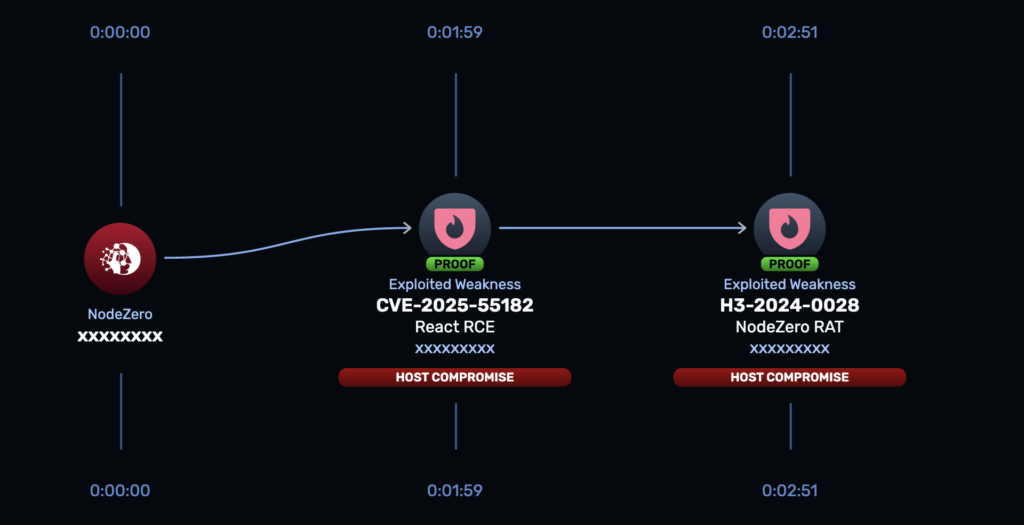
CVE-2025-55182 is a logical deserialization flaw in the RSC Flight protocol. A malicious Flight payload can bypass validation and reach internal execution paths that evaluate attacker-controlled input. This enables unauthenticated remote code execution with a single crafted HTTP request.
Once exploited, attackers gain control of the application server that renders pages and executes server functions. They can steal credentials, implant backdoors or pivot deeper into backend systems.
Stop Guessing, Start Proving
Key technical characteristics:
- CVSS 10.0 unauthenticated remote code execution
- Affects React versions 19.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1 and 19.2.0
- Patched in React versions 19.0.1, 19.1.2 and 19.2.1
- Exploitable when RSC or server function endpoints are reachable
- Impacts any framework that integrates the vulnerable server packages
A Note on CVE-2025-66478
Next.js initially requested the identifier CVE-2025-66478 to track the downstream impact of this vulnerability in the Next.js App Router. MITRE later rejected this identifier as a duplicate of CVE-2025-55182. There is only one underlying vulnerability.
Active exploitation and real-world exposure
Threat intelligence teams observed exploitation attempts within hours of public disclosure, including activity linked to China-nexus actors such as Earth Lamia and Jackpot Panda. Internet-wide scanning increased immediately after the initial advisory.
CISA added CVE-2025-55182 to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog, elevating the urgency for both patching and verification.
Exploitability varies based on deployment. Many React-based applications do not expose RSC endpoints by default, while others rely on rendering models that reduce exposure. This makes verification essential.
Quick actions to take now
1. Run the NodeZero Rapid Response test
The Rapid Response test determines whether CVE-2025-55182 is exploitable inside your environment. This helps teams make informed decisions rather than react to headline-driven assumptions.
2. Patch React, Next.js and related frameworks
React: update to 19.0.1, 19.1.2 or 19.2.1
Next.js: upgrade to patched releases such as 15.0.5, 15.1.9, 15.2.6, 15.3.6, 15.4.8, 15.5.7 or 16.0.7
Other frameworks with RSC integrations should follow their respective advisories.
3. Re-run the Rapid Response test
NodeZero confirms whether previously exploitable paths have been eliminated and whether mitigations are effective.
Indicators of compromise
Vendor-issued IoCs remain limited. Until more specific guidance is available, organizations can monitor for common RCE behaviors:
- Unexpected POST traffic to RSC or server function endpoints
- Errors or logs involving malformed Flight payloads
- Creation of unfamiliar modules or temporary files
- Outbound connections initiated by application servers
- Execution of reconnaissance commands originating from the server process
These should be used alongside threat intelligence and detection rules as they emerge.
Affected versions and patch information
React
Affected: 19.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, 19.2.0
Patched: 19.0.1, 19.1.2, 19.2.1
Next.js
Affected: 14.3.0-canary.77 and later canaries, plus unpatched 15.x and 16.x App Router releases
Patched examples: 15.0.5, 15.1.9, 15.2.6, 15.3.6, 15.4.8, 15.5.7, 16.0.7
Other frameworks
React Router RSC preview, Remix RSC integrations, Waku, Vite RSC plugin, Parcel RSC plugin, RedwoodSDK and other RSC-enabled frameworks may require separate updates.
Timeline
- November 29, 2025 — Researcher Lachlan Davidson reports the vulnerability to React.
- December 3, 2025 — React publishes an advisory and patches for CVE-2025-55182, covering React 19.0, 19.1.0, 19.1.1, and 19.2.0, and fixing them in 19.0.1, 19.1.2, and 19.2.1.
- December 3–4, 2025 — SecurityWeek, Dark Reading, The Hacker News, and BleepingComputer publish analyses of React2Shell, confirming unauthenticated RCE, CVSS 10, and significant cloud-scale exposure.
- December 5, 2025 — NodeZero React Server RCE Rapid Response test becomes generally available to customers.
- December 5, 2025 — CVE-2025-55182 assigned to CISA KEV.
References
🔗 React advisory for CVE-2025-55182 (React Server Components / Flight RCE)
🔗 SecurityWeek — “React2Shell: In-the-Wild Exploitation Expected for Critical React Vulnerability”
🔗 BleepingComputer — “Critical React, Next.js flaw lets hackers execute code on servers”
🔗 Dark Reading — “Critical React Flaw Triggers Calls for Immediate Action”