CVE-2025-49844
Redis Lua Use-After-Free Vulnerability | Critical RCE Risk
CVE-2025-49844 is an authenticated remote code execution vulnerability in the Lua scripting engine of Redis, the open-source in-memory data store widely used around the world to store ephemeral data and manage caching & user sessions.
The flaw allows an authenticated user to execute arbitrary code through a specially crafted Lua script that manipulates the garbage collector. Redis disclosed the issue on October 3, 2025, as part of an ongoing effort by the Redis community to maintain security and compliance.
Redis assigned the issue a CVSS 3.1 base score of 10.0 (Critical). While exploitation requires valid credentials, authentication is not required by default, so many Redis instances are configured without needing to login. Organizations who use Redis both externally and internally without authentication configured are at significant risk of exploitation, though no active exploitation has been observed.
Technical Details
- CVE-2025-49844 results from improper memory handling in Redis’ Lua engine when processing garbage-collected objects.
- An attacker with access can craft and send a malicious Lua script to trigger a use-after-free condition, leading to arbitrary code execution.
- Successful exploitation could allow full remote control of the Redis instance, enabling attackers to further escalate privileges, install malware, or exfiltrate data, and move deeper into the organization.
- Redis rated the flaw at CVSS 10.0 due to the potential for full compromise once authentication is achieved.
NodeZero® Offensive Security Platform — Rapid Response
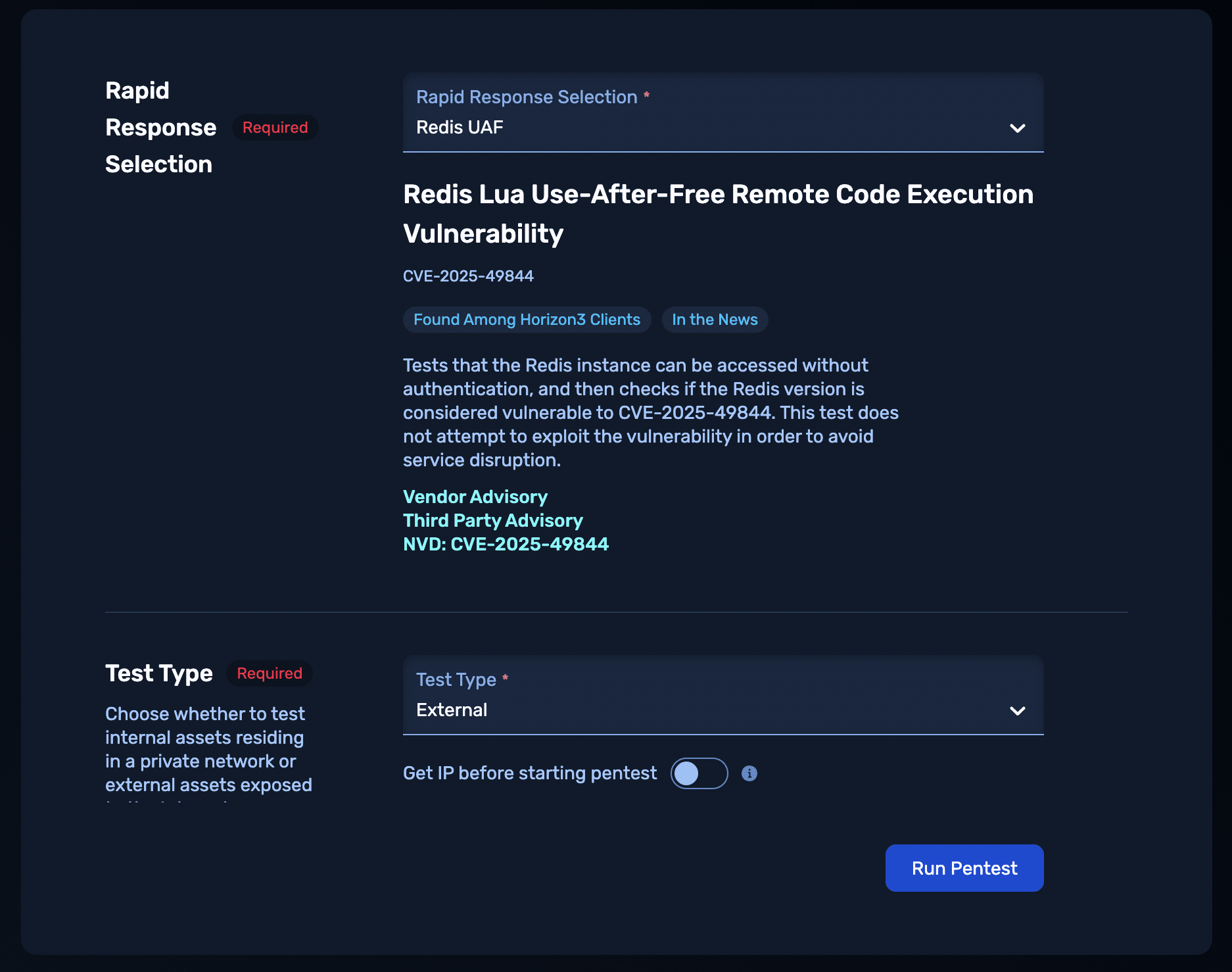
The Redis Rapid Response test, released October 9, 2025, enables customers to safely check if they are at risk.
- Run the Rapid Response test — Horizon3.ai customers: run the NodeZero Rapid Response test from the customer portal to determine whether any Redis instances are vulnerable and unauthenticated.
Note: In order to maintain production safety, this Rapid Response test does not attempt to exploit the issue. It instead relies on the service’s self-reported version number.
- Patch immediately — upgrade to the latest fixed Redis versions listed below. If patching is delayed, restrict access to trusted management IPs, enable protected mode, and enforce strong authentication for all instances.
Indicators of Compromise
| Indicator | Type | Description |
| Unauthorized access to Redis | Behavior | Connections from unknown IPs or users not normally accessing Redis |
| Unknown or anomalous Lua scripts | Behavior | Presence of unexpected or suspicious Lua code in the Redis database |
| Redis server crash logs | Behavior | Crashes or stack traces originating from the Lua engine |
| Unexpected command execution | Behavior | Unusual process activity or command execution by the redis-server user |
| Unusual network traffic | Behavior | Ingress or egress traffic anomalies from Redis hosts |
| File system changes | Behavior | Unexpected modifications to directories containing Redis configuration or persistent data |
Find risk exposure with Rapid Response Test
Affected versions & patch
- Affected:
- All Redis Software releases prior to:
- 7.22.2-12 and above
- 7.8.6-207 and above
- 7.4.6-272 and above
- 7.2.4-138 and above
- 6.4.2-131 and above
- All Redis OSS/CE/Stack releases with Lua scripting prior to:
- OSS/CE: 8.2.2+, 8.0.4+, 7.4.6+, 7.2.11+
- Stack: 7.4.0-v7+, 7.2.0-v19+
- All Redis Software releases prior to:
- Patch: Upgrade to the versions listed above to remediate the vulnerability. Redis Cloud users are already protected, as the hosted platform has been patched.
References
🔗 Redis GitHub Security Advisories page
🔗 OpenCVE